CRAC creation context#
Introduction#
When OpenRAO tries to import a native CRAC file (FlowBasedConstraint, CSE, CIM, …)
into an internal CRAC format, some data transformation can happen, and data present in the final CRAC object
will not be a “one-to-one” exact representation of the data in the original file.
This can be an issue for the final user, as querying the RAO result file or object
needs knowledge of the artefacts OpenRAO created during CRAC creation.
The CracCreationContext
classes produced by the different CRAC creators allow the user to access meta-information
about the CRAC creation process, and to map the original file to the created artifacts in the OpenRAO object, or to
error messages if some objects could not be imported.
This is particularly useful if the user needs to export the RAO result in a format different from OpenRAO’s internal format,
and to reference CNECs and remedial actions as they were defined in the original (native) CRAC file.
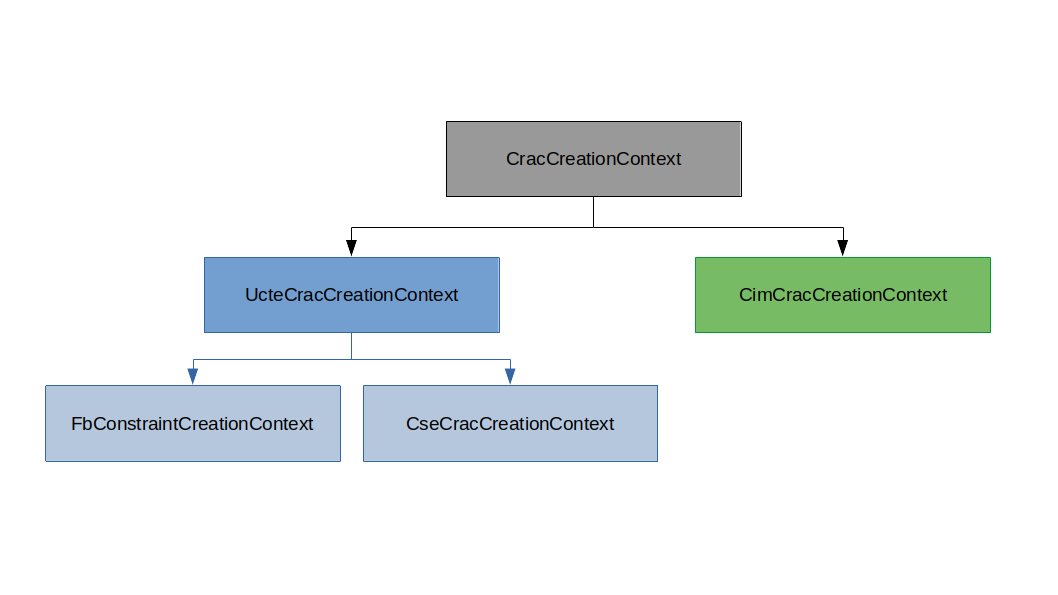
Many implementations of CracCreationContext exist, depending on the original format. Every implementation has its own
specific API. CracCreationContexts are the main output of CracCreators.
Network network = ...
NativeCrac nativeCrac = NativeCracImporters.importData(Paths.get("/example_file.xml"));
OffsetDateTime timestamp = ...
CracCreationContext cracCreationContext = CracCreators.createCrac(nativeCrac, network, timestamp);
Non-specific information#
All CracCreationContext implementations present the following information.
CRAC creation success#
A simple boolean set to true if a OpenRAO CRAC could be created from the native CRAC file.
boolean success = cracCreationContext.isCreationSuccessful();
CRAC object#
The created CRAC object, to be used in the RAO.
Crac crac = cracCreationContext.getCrac();
Timestamp#
When applicable, this field contains the timestamp for which the CRAC has been created from the original CRAC file (as
some CRAC formats, such as FlowBasedConstraint, can support constraint definition for multiple timestamps).
This field can be useful if the timestamp needs to be exported in a custom results file.
cracCreationContext.getTimeStamp();
Network name#
Contains the name of the network that was used to create the CRAC object.
cracCreationContext.getNetworkName();
CRAC creation report#
A textual report that can usefully be logged. It contains information about elements that were ignored or modified in the
original CRAC.
The report’s lines all begin with one of these tags:
[ERROR]: happens when a CRAC could not be created (e.g. if the user tried to import a FlowBasedConstraint file without defining a timestamp, or a CSE file with a non-UCTE network file, etc.)
[REMOVED]: happens when OpenRAO ignores elements of the CRAC because they cannot be imported, or because they are not relevant for the RAO (e.g. if a contingency is defined on an element that doesn’t exist in the network, or if a CNEC is neither optimized nor monitored, etc.)
[ADDED]: happens if OpenRAO decides to add elements that were not explicitly defined in the original file (e.g. if the CRAC contains AUTO CNECs without any remedial action associated, OpenRAO will automatically duplicate them in the outage instant in order to secure them during the preventive RAO)
[ALTERED]: happens if OpenRAO imports an element after altering it or ignoring some of its components (e.g. if a monitored element shall be so after multiple contingencies, among which some were not imported for any reason, then only valid contingencies will be used for the created CNECs)
[WARN]: non-critical warnings (e.g. if the user defined a timestamp for a CRAC format that doesn’t require one, the timestamp is ignored and a warning is logged)
[INFO]: non-critical information
The final user shall check these messages to ensure that their CRAC file is well-defined.
cracCreationContext.getCreationReport().printCreationReport();
UCTE implementation#
A common UCTE interface UcteCracCreationContext
has been defined in order to collect the common fields a CracCreationContext implementation should hold when created using a UCTE network.
Of course, not all CRAC formats use UCTE convention, so not all CRAC formats can implement this UCTE interface.
Currently, this interface is implemented by FlowBasedConstraint and CSE crac creators.
It has all the non-specific features, plus the following.
Branch CNEC creation contexts#
The BranchCnecCreationContext contains information about the creation of CNECs in OpenRAO. One BranchCreationContext is created for every native CNEC-equivalent element in the original CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native object in the original CRAC. Depending on the CRAC implementation, OpenRAO can construct this by concatenating multiple elements in order to ensure the ID is unique in the file.
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import one or multiple CNECs from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this CNEC when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
NativeBranch is the UCTE branch referred to in the original CRAC, with a “from” node, a “to” node, and a suffix (order code or alias)
isBaseCase is a boolean equal to true if the CNEC has been created for the preventive instant
ContingencyId (if present) is the ID of the contingency for which the CNEc is monitored
CreatedCnecIds holds the ID(s) of the OpenRAO CNEC(s) that were created for this native critical branch. These are the IDs the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
isDirectionInvertedInNetwork is a boolean equal to true if the from/to in the original CRAC are the inverse of the PowSyBl network’s from/to. This means that OpenRAO had to invert the branch when importing it (in order to be coherent with the network) as well as its flow constraints, and that the flow results in the RaoResult will be inverted in regard to the original CRAC’s convention. The user should be careful to invert these results before exploiting them.
Here is a complete example of BranchCnecCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
UcteCracCreationContext ucteCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all native CNEC results
ucteCracCreationContext.getBranchCnecCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, ucteCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific native CNEC called "BranchCnecFR_1"
BranchCnecCreationContext context = ucteCracCreationContext.getBranchCnecCreationContext("BranchCnecFR_1");
printSomeResults(context, ucteCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(BranchCnecCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Native critical branch ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
System.out.println(String.format("Native line: %s %s %s", context.getNativeBranch().getFrom(), context.getNativeBranch().getTo(), context.getNativeBranch().getSuffix()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The native branch could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
double flowMultiplier;
if (context.isDirectionInvertedInNetwork()) {
System.out.println(String.format("In the network the line is called %s %s %s, so all its results will be inverted!", context.getNativeBranch().getTo(), context.getNativeBranch().getFrom(), context.getNativeBranch().getSuffix()));
flowMultiplier = -1.;
} else {
flowMultiplier = 1.;
}
if (context.isBaseCase()) {
System.out.println("Monitored in preventive only");
} else {
System.out.println(String.format("Monitored after contingency: %s", context.getContingencyId().get()));
}
context.getCreatedCnecsIds().entrySet().forEach(entry -> {
System.out.println(String.format("Created CNEC for instant %s: %s", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
FlowCnec flowCnec = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getFlowCnec(entry.getValue());
System.out.println(String.format("The left-side flow on this native critical branch after RAO is: %.2f A", flowMultiplier * raoResult.getFlow(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(flowCnec.getState()), flowCnec, Side.LEFT, Unit.AMPERE)));
System.out.println(String.format("The right-side flow on this native critical branch after RAO is: %.2f A", flowMultiplier * raoResult.getFlow(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(flowCnec.getState()), flowCnec, Side.RIGHT, Unit.AMPERE)));
System.out.println(String.format("The flow margin on this native critical branch after RAO is: %.2f A", raoResult.getMargin(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(flowCnec.getState()), flowCnec, Unit.AMPERE)));
}
);
}
Remedial action creation contexts#
The RemedialActionCreationContext contains information about the creation of remedial actions in OpenRAO. One RemedialActionCreationContext is created for every native remedial-action element in the original CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native object in the original CRAC. Depending on the CRAC implementation, OpenRAO can construct this by concatenating multiple elements in order to ensure the ID is unique in the file.
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import a remedial action from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this remedial action when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedRAId holds the ID of the OpenRAO remedial action that was created from this native element. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of RemedialActionCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
UcteCracCreationContext ucteCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all native remedial action results
ucteCracCreationContext.getRemedialActionCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, ucteCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific native remedial action called "RemedialAction656"
RemedialActionCreationContext context = ucteCracCreationContext.getRemedialActionCreationContext("RemedialAction656");
printSomeResults(context, ucteCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(RemedialActionCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Native remedial action ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The remedial action could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The remedial action created in the OpenRAO CRAC is called: %s", context.getCreatedRAId()));
RemedialAction<?> remedialAction = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getRemedialAction(context.getCreatedRAId());
cracCreationContext.getCrac().getStates().forEach(state -> {
String stateDescription = String.format("instant %s%s", state.getInstant(), state.isPreventive() ? "" : " after contingency " + state.getContingency().get().getId());
if (raoResult.getActivatedNetworkActionsDuringState(state).contains(remedialAction)) {
// Remedial action is a network action, it has been activated in this state
System.out.println(String.format("The network action has been selected by RAO at %s", stateDescription));
} else if (raoResult.getActivatedRangeActionsDuringState(state).contains(remedialAction)) {
// Remedial action is a range action, it has been activated in this state. We can query its optimal set-point.
System.out.println(String.format("The range action has been selected by RAO at %s, with optimal set-point %.2f", stateDescription, raoResult.getOptimizedSetPointOnState(state, (RangeAction<?>) remedialAction)));
}
});
}
FlowBasedConstraint implementation#
The FbConstraintCreationContext is a UcteCracCreationContext implementation with no extra features.
CSE implementation#
The CseCracCreationContext is a UcteCracCreationContext implementation with one extra feature for contingencies.
Outage creation contexts#
The CseOutageCreationContext contains information about the creation of contingencies in OpenRAO. One CseOutageCreationContext is created for every native “Outage” element in the original CSE CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native Outage (contained in the “Name” tag)
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import a contingency from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this contingency when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedContingencyId holds the ID of the OpenRAO contingency that was created from this native element. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of CseOutageCreationContext usage:
CseCracCreationContext cseCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Print some information about all native Outage elements
cseCracCreationContext.getOutageCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeInformation(context, cseCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the information about a specific Outage called "Outage123"
CseOutageCreationContext context = cseCracCreationContext.getRemedialActionCreationContext("Outage123");
printSomeInformation(context, cseCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeInformation(CseOutageCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Native outage ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The outage could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any more information for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The contingency created in the OpenRAO CRAC is called: %s", context.getCreatedContingencyId()));
Contingency contingency = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getContingency(context.getCreatedContingencyId());
cracCreationContext.getCrac().getStates(contingency).forEach(state -> {
System.out.println(String.format("The contingency is monitored at instant %s", state.getInstant()));
System.out.println(String.format("At this instant, and after this contingency, %s CNECs are monitored by the RAO", cracCreationContext.getCrac().getCnecs(state).size()));
});
}
CIM implementation#
The CimCracCreationContext
is not a UcteCracCreationParameters implementation.
It has all the non-specific features, plus the following.
Contingency series creation contexts#
The CimContingencyCreationContext contains information about the creation of contingencies in OpenRAO. One CimContingencyCreationContext is created for every B55 “Contingency_Series” element in the original CSE CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native Contingency_Series (contained in the “mRID” tag)
NativeName is the user-friendly name of the native Contingency_Series (contained in the “name” tag)
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import a contingency from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this contingency when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedContingencyId holds the ID of the OpenRAO contingency that was created from this native element. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of CimContingencyCreationContext usage:
CimCracCreationContext cimCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Print some information about all native Contingency_Series elements
cimCracCreationContext.getContingencyCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeInformation(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the information about a specific Contingency_Series with mRID "CO-125"
RemedialActionCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getContingencyCreationContextById("CO-125");
printSomeInformation(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
// Query the information about a specific Contingency_Series with name "N-1 on FR-ES branch"
RemedialActionCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getContingencyCreationContextByName("N-1 on FR-ES branch");
printSomeInformation(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeInformation(CimContingencyCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Native Contingency_Series ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
System.out.println(String.format("Native Contingency_Series name: %s", context.getNativeName()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The Contingency_Series could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any more information for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The contingency created in the OpenRAO CRAC is called: %s", context.getCreatedContingencyId()));
Contingency contingency = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getContingency(context.getCreatedContingencyId());
cracCreationContext.getCrac().getStates(contingency).forEach(state -> {
System.out.println(String.format("The contingency is monitored at instant %s", state.getInstant()));
System.out.println(String.format("At this instant, and after this contingency, %s CNECs are monitored by the RAO", cracCreationContext.getCrac().getCnecs(state).size()));
});
}
Monitored series creation contexts#
The MonitoredSeriesCreationContext contains information about the creation of CNECs in OpenRAO. One MonitoredSeriesCreationContext is created for every native B57 “Monitored_Series” in the original CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native Monitored_Series (contained in the “mRID” tag)
NativeName is the user-friendly name of the native Monitored_Series (contained in the “name” tag)
NativeResourceId is the ID of the network element monitored by the Monitored_Series (contained in the “RegisteredResource/mRID” tag)
NativeResourceName is the user-friendly name of the network element monitored by the Monitored_Series (contained in the “RegisteredResource/name” tag)
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import one or multiple CNECs from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this CNEC when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedCnecIds holds the ID(s) of the OpenRAO CNEC(s) that were created for this native critical branch. These are the IDs the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
MeasurementCreationContexts is a set of MeasurementCreationContext objects. One MeasurementCreationContexts is created for every “Measurements” tag inside the Monitored_Series. In fact, one “Measurement” can create multiple OpenRAO CNECs, depending on the contingencies and instants defined for the Monitored_Series in the CIM CRAC (see here fore more detail). Every MeasurementCreationContext contains the following information:
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import at least one CNEC from this “Measurements”.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CnecCreationContexts is a map containing, for every state (i.e. (Instant, Contingency) pair), up to one CnecCreationContext . Every CnecCreationContext holds the following information:
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import a CNEC from this “Measurements”, for the given contingency & instant.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
CreatedCnecIds holds the ID of the OpenRAO CNEC that was created (if applicable) from this “Measurements”, for the given contingency & instant. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of MonitoredSeriesCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
CimCracCreationContext cimCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all native Monitored_Series results
cimCracCreationContext.getMonitoredSeriesCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific Monitored_Series with mRID "MR-10"
MonitoredSeriesCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getMonitoredSeriesCreationContext("MR-10");
printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(MonitoredSeriesCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Native Monitored_Series ID & name: %s - %s", context.getNativeId(), context.getNativeName()));
System.out.println(String.format("Monitored network element ID & name: %s - %s", context.getNativeResourceId(), context.getNativeResourceName()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The Monitored_Series could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("This Monitored_Series created %s CNECs in the OpenRAO CRAC", context.getCreatedCnecIds().size()));
context.getMeasurementCreationContexts().forEach(measurementContext -> {
if (!measurementContext.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("One Measurement has not been imported for the following reason: %s - %s", measurementContext.getImportStatus(), measurementContext.getImportStatusDetail()));
} else {
measurementContext.getCnecCreationContexts().forEach((k, v) -> {
if (v.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("Created CNEC ID for instant %s, after contingency %s, is %s", k.getKey(1), k.getKey(0), v.getCreatedCnecId()));
FlowCnec flowCnec = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getFlowCnec(v.getCreatedCnecId());
System.out.println(String.format("Its flow margin after RAO is: %.2f MW", raoResult.getMargin(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(flowCnec.getState()), flowCnec, Unit.MEGAWATT)));
} else {
System.out.println(String.format("The CNEC could not be created for instant %s, after contingency %s, for the following reason: %s - %s", k.getKey(1), k.getKey(0), v.getImportStatus(), v.getImportStatusDetail()));
}
});
}
});
}
Angle CNEC creation contexts#
The AngleCnecCreationContext contains information about the creation of angle CNECs in OpenRAO. One AngleCnecCreationContext is created for every native B56 “AdditionalConstraint_Series” in the original CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native AdditionalConstraint_Series (contained in the “mRID” tag)
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import one or multiple CNECs from this element.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedCnecId is the ID of the OpenRAO angle CNEC that was created for this AdditionalConstraint_Series. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
ContingencyId holds the ID of the contingency for this angle CNEC. It can be used with internal objects.
Here is a complete example of AngleCnecCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
CimCracCreationContext cimCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all native AdditionalConstraint_Series results
cimCracCreationContext.getAngleCnecCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific AdditionalConstraint_Series with mRID "AC-100"
AngleCnecCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getAngleCnecCreationContext("AC-100");
printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(AngleCnecCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("AdditionalConstraint_Series ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The angle CNEC could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The angle CNEC created in the OpenRAO CRAC is called: %s", String.join(", ", context.getCreatedAngleCnecId())));
AngleCnec angleCnec = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getAngleCnec(context.getCreatedAngleCnecId());
// Print its angle value (note that this will not work with the default search-tree RAO implementation)
System.out.println(String.format("Its angle value after RAO is: %.2f", raoResult.getAngle(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(angleCnec.getState()), angleCnec, Unit.DEGREE)));
}
Voltage CNEC creation contexts#
The VoltageCnecCreationContext contains information about the creation of angle CNECs in OpenRAO. One VoltageCnecCreationContext is created for every voltage CNEC that should be created, as configured in the CimCracCreationParameters. It holds the following information:
NativeNetworkElementId is the unique identifier of the network element that is monitored
Instant is the instant for which the CNEC is created
NativeContingencyName is the name of the contingency for which the CNEC is created (if instant is not preventive), as defined in the “name” field of the B55 Contingency_Series
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import the voltage CNEC
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
CreatedCnecId is the ID of the OpenRAO voltage CNEC that was created. This is the ID the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of VoltageCnecCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
CimCracCreationContext cimCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all voltage CNECs results
cimCracCreationContext.getVoltageCnecCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific voltage CNEC that was created for network element "ne1", at instant "curative", after contingency "co1"
VoltageCnecCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getVoltageCnecCreationContext("ne1", Instant.CURATIVE, "co1");
printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(VoltageCnecCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("Voltage CNEC for network element %s after contingency %s at instant %s", context.getNativeNetworkElementId(), context.getNativeContingencyName(), context.getInstant()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The voltage CNEC could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The voltage CNEC created in the OpenRAO CRAC is called: %s", String.join(", ", context.getCreatedCnecId())));
VoltageCnec voltageCnec = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getVoltageCnec(context.getCreatedCnecId());
// Print its voltage value (note that this will not work with the default search-tree RAO implementation)
System.out.println(String.format("Its angle value after RAO is: %.2f", raoResult.getVoltage(OptimizationState.afterOptimizing(voltageCnec.getState()), voltageCnec, Unit.KILOVOLT)));
}
Remedial action series creation contexts#
The CIM RemedialActionSeriesCreationContext contains information about the creation of remedial actions in OpenRAO. One RemedialActionSeriesCreationContext is created for every B56 “RemedialAction_Series” element in the original CRAC, that can be uniquely identified. It holds the following information:
NativeId is the unique identifier of the native RemedialAction_Series (contained in the “mRID” tag)
isImported is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO was able to import a remedial action from this element.
isAltered is a boolean equal to true if OpenRAO had to alter some elements of this remedial action when importing it.
ImportStatus contains further information about the import status of the element (see appendix)
ImportStatusDetail is a user-friendly message explaining why the element has not been imported (if applicable)
isInverted is a boolean equal to true if the imported remedial action had to be inverted with regard to the original CRAC convention, in order to comply with the PowSyBl network convention (this is especially useful for HVDC range actions). If this field is set to true, the user should be careful to invert results accordingly (see example below).
CreatedIds holds the IDs of the OpenRAO remedial actions that were created from this native element (generally holds up to one ID, except for HVDC range actions where it can hold multiple IDs). These are the IDs the user should use to query the internal CRAC & RaoResult objects.
Here is a complete example of RemedialActionSeriesCreationContext usage to export user-comprehensible RAO results:
CimCracCreationContext cimCracCreationContext = ...
RaoResult raoResult = ...
// Do a custom results export of all native remedial action results
cimCracCreationContext.getRemedialActionSeriesCreationContexts().foreach(context -> printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult));
// Query the results of a specific RemedialAction_Series with mRID "PRA_5"
RemedialActionSeriesCreationContext context = cimCracCreationContext.getRemedialActionSeriesCreationContext("PRA_5");
printSomeResults(context, cimCracCreationContext, raoResult);
void printSomeResults(RemedialActionSeriesCreationContext context, CracCreationContext cracCreationContext, RaoResult raoResult) {
System.out.println(String.format("RemedialAction_Series ID: %s", context.getNativeId()));
if (!context.isImported()) {
System.out.println(String.format("The remedial action could not be imported by OpenRAO for the following reason: %s - %s", context.getImportStatus(), context.getImportStatusDetail()));
System.out.println("The element has been ignored by the RAO, we cannot access any result for it!");
return;
}
System.out.println(String.format("The remedial action(s) created in the OpenRAO CRAC is (are) called: %s", String.join(", ", context.getCreatedIds())));
context.getCreatedIds().forEach(createdRaId -> {
System.out.println(String.format("Remedial action %s:", createdRaId));
RemedialAction<?> remedialAction = cracCreationContext.getCrac().getRemedialAction(createdRaId);
cracCreationContext.getCrac().getStates().forEach(state -> {
String stateDescription = String.format("instant %s%s", state.getInstant(), state.isPreventive() ? "" : " after contingency " + state.getContingency().get().getId());
if (raoResult.getActivatedNetworkActionsDuringState(state).contains(remedialAction)) {
// Remedial action is a network action, it has been activated in this state
System.out.println(String.format("The network action has been selected by RAO at %s", stateDescription));
} else if (raoResult.getActivatedRangeActionsDuringState(state).contains(remedialAction)) {
// Remedial action is a range action, it has been activated in this state. We can query its optimal set-point.
int multiplier = context.isInverted() ? -1 : 1;
System.out.println(String.format("The range action has been selected by RAO at %s, with optimal set-point %.2f", stateDescription, multiplier * raoResult.getOptimizedSetPointOnState(state, (RangeAction<?>) remedialAction)));
}
});
});
}
Appendix#
Elementary import status#
ImportStatus
is an enum field that can be used in the API to filter elements that were not imported for different reasons.
For instance, the user may choose to write information about CNECs that were not imported because they are not useful in
the RAO (“NOT_FOR_RAO”), but ignore the other ones.
Here are the possible values of this enum:
IMPORTED: the element was successfully imported
ELEMENT_NOT_FOUND_IN_NETWORK: the element references a network element that was not found in the network (e.g. a critical branch defined on a line that does not exist in the PowSyBl network)
INCOMPLETE_DATA: the element is missing crucial information needed to define a complete OpenRAO object (e.g. a flow CNEC defined without a flow limit)
INCONSISTENCY_IN_DATA: the element definition is inconsistent (e.g. a PST range action that is defined on a non-PST network element)
NOT_YET_HANDLED_BY_OPEN_RAO: the business element is not yet supported by OpenRAO (e.g. line impedance remedial-actions are not yet supported)
NOT_FOR_RAO: the element is ignored because it will not be used in the RAO (e.g. critical branches that are neither optimized nor monitored)
NOT_FOR_REQUESTED_TIMESTAMP: the element is ignored because it does not apply to the given timestamp
OTHER: any error that does not fall into one of the categories above